Table of Contents
|
Introduction
The FILTER function in Excel is a powerful tool that allows
users to extract specific data from a range based on defined criteria. This
function simplifies the process of analyzing and manipulating large datasets by
enabling you to display only the information that meets certain conditions. In
this article, we will explore the FILTER function in detail, including
its syntax, uses, and along with ten examples using student performance data.
Whether you're a beginner or looking to enhance your Excel skills, this guide
will take you from novice to expert in no time!
Syntax
of the Filter Function
The syntax of the FILTER function is straightforward. Here’s
how it looks:
=FILTER(array, include, [if_empty])
Parameters:
- array: This is the range of data you
want to filter. It includes all the columns you wish to extract.
- include: This parameter specifies the
condition(s) that must be met for the data to be included in the result.
It should return TRUE or FALSE values.
- [if_empty]: This
optional parameter allows you to specify a value to return if no data
meets the criteria.
Uses
of the Filter Function
The FILTER function can be used for various tasks, such as:
- Displaying subsets of data based on
specific conditions.
- Analyzing student performance by grade,
score, or attendance.
- Creating dynamic reports that update
automatically as data changes.
With the basic understanding of the FILTER function, let's
explore practical examples using a dataset containing student information.
10
Examples Using the Filter Function
Below is a dataset of student performance:
1. Filter by Grade
To show only the students who are in grade 10, we can use the FILTER
function. This function allows us to extract rows that meet specific
conditions. The formula to filter for grade 10 is:
=FILTER(A2:O11, D2:D11=10)
In this formula, A2:O11 represents the range of data we want to
filter, and D2:D11=10 is the condition specifying that we only want students in
grade 10. When you enter this formula, Excel will return all rows from the
dataset where the grade is 10, making it easy to focus on these students.
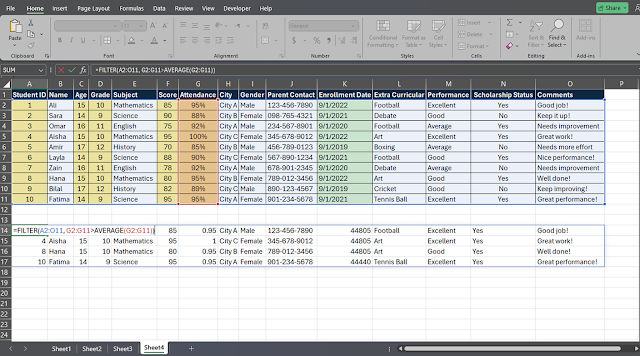
2. Filter by City
If you want to get a list of students from a specific city, say
City A, you would use the following formula:
=FILTER(A2:O11, H2:H11="City A")
Here, H2:H11="City A" is the condition that filters for
students living in City A. This formula extracts all relevant rows, allowing
you to analyze or report specifically on students from that city.
3. Filter by Score Above 80
To find students who scored above 80, you can apply the FILTER
function like this:
=FILTER(A2:O11, F2:F11>80)
In this case, F2:F11>80 checks the score column to see which
students have scores greater than 80. The result will be a list of all students
who achieved this score, helping you identify high achievers.
4. Combine FILTER with COUNTA
If you want to count how many students scored above 80, you can
combine FILTER with COUNTA like this:
=COUNTA(FILTER(A2:A11, F2:F11>80))
This formula first filters the student list to find those with scores above 80 and then counts how many entries are in that filtered list. The result will give you the total number of students who excelled.
5. Filter by Scholarship Status
To list students who received scholarships, use the following
formula:
=FILTER(A2:O11, N2:N11="Yes")
In this example, N2:N11="Yes" is the condition that filters for students with a scholarship status of "Yes." The output will display all the students who have received scholarships, making it easy to view this group.
6. Filter by Enrollment Date
If you're interested in listing students who enrolled after January
1, 2021, the formula would be:
=FILTER(A2:O11, K2:K11>DATE(2021,1,1))
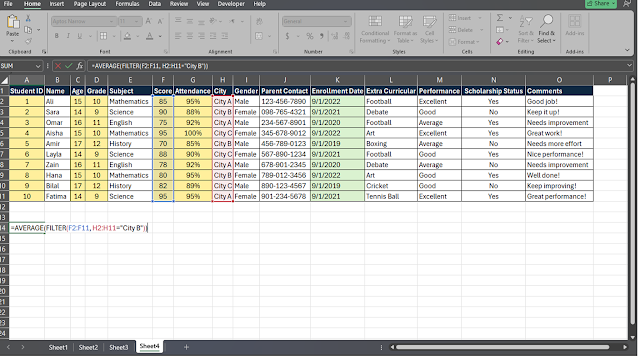
7. Combine FILTER with AVERAGE
To calculate the average score of students from City B, you can
combine FILTER with the AVERAGE function:
=AVERAGE(FILTER(F2:F11, H2:H11="City B"))
In this formula, FILTER retrieves scores of students from City B, and AVERAGE computes the average of these scores. This provides insights into the performance of students specifically from City B.
8. Filter for Recent Enrollments
To show students who enrolled in the last year, you can use:
=FILTER(A2:O11, K2:K11>=DATE(YEAR(TODAY())-1,1,1))
This formula checks the enrollment date column to find students who enrolled on or after January 1 of the previous year. It's useful for tracking new enrollments within a specific timeframe.
9. Filter for Above Average Attendance
To find students with above-average attendance, use this formula:
=FILTER(A2:O11, G2:G11>AVERAGE(G2:G11))
This formula first calculates the average attendance using AVERAGE(G2:G11)
and then filters the list to find students with attendance greater than this
average. This helps identify students who are more consistently present.
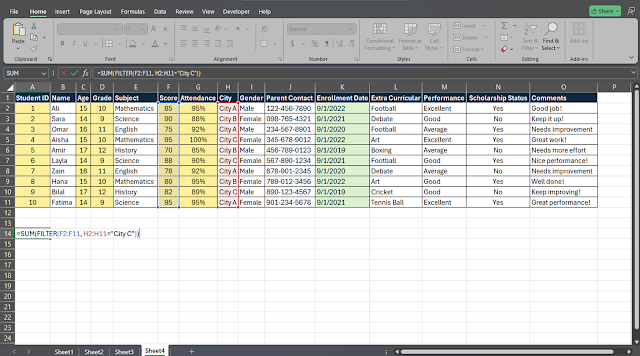
10. Filter and Aggregate Score
To calculate the total score of students in City C, you would use:
=SUM(FILTER(F2:F11, H2:H11="City C"))
Here, FILTER extracts the scores of students from City C, and SUM
adds them together. The result gives you the total score for all students in
that city, allowing for quick performance assessments.
Conclusion
The FILTER function is a versatile tool that allows you to
manipulate and analyze data effectively in Excel. By learning how to use this
function with practical examples, you can quickly become proficient in handling
datasets, whether for academic, business, or personal purposes. With the skills
gained from this guide, you can efficiently extract and analyze data to make
informed decisions. Start practicing the examples provided and explore further
possibilities with the FILTER function!
Click here to download template













No comments:
Post a Comment